DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development and IT operations. It aims to shorten the systems development life cycle and
provide continuous delivery with high software quality. DevOps is complementary to agile software development; several DevOps aspects came from the
agile way of working.
DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increases an organization’s ability to deliver applications and
services at high velocity: evolving and improving products at a faster pace than organizations using traditional software development and infrastructure
management processes. This speed enables organizations to better serve their customers and compete more effectively in the market.
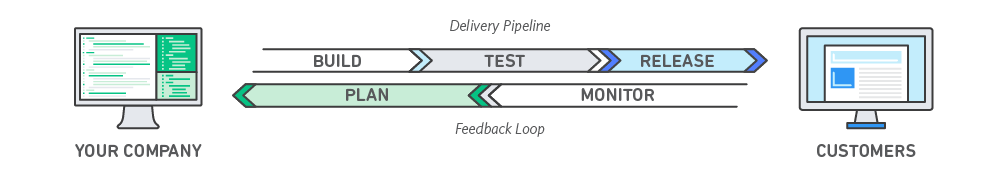
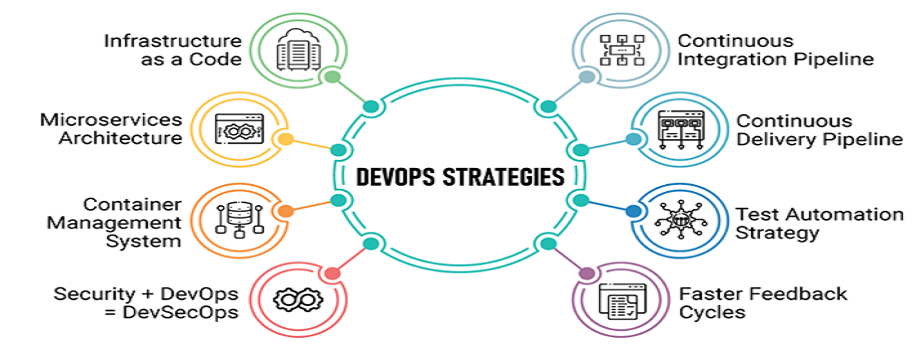
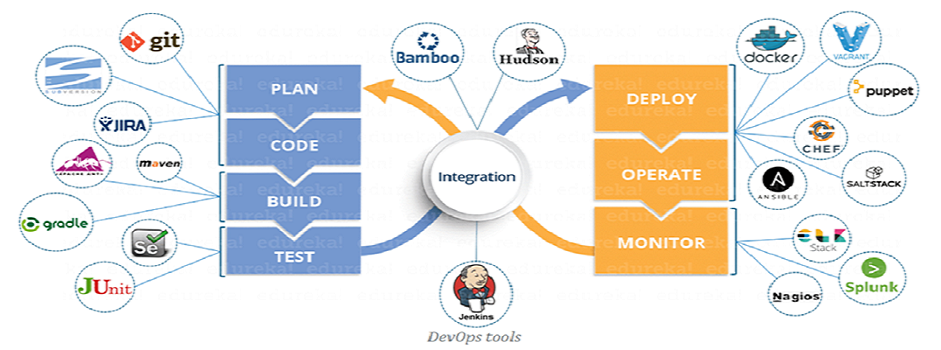
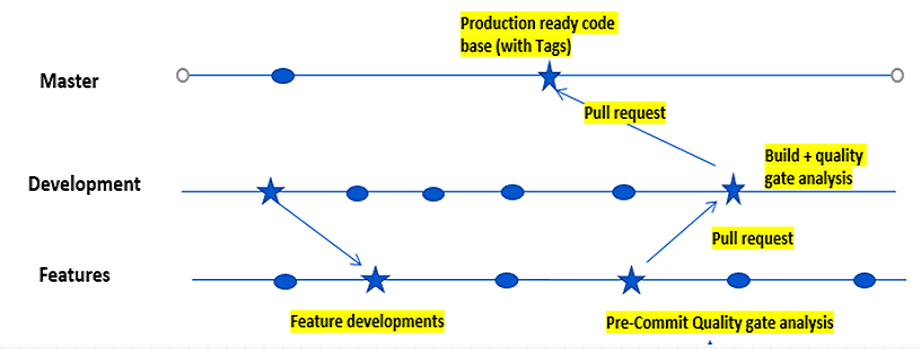
How DevOps Works
Under a DevOps model, development and operations teams are no longer “siloed.” Sometimes, these two teams are merged into a single team where the engineers work across the entire application lifecycle, from development and test to deployment to operations, and develop a range of skills not limited to a single function.
In some DevOps models, quality assurance and security teams may also become more tightly integrated with development and operations and throughout the application lifecycle. When security is the focus of everyone on a DevOps team, this is sometimes referred to as DevSecOps.
These teams use practices to automate processes that historically have been manual and slow. They use a technology stack and tooling which help them operate and evolve applications quickly and reliably. These tools also help engineers independently accomplish tasks (for example, deploying code or provisioning infrastructure) that normally would have required help from other teams, and this further increases a team’s velocity.